The Benefits of HTML5-Based Video Delivery
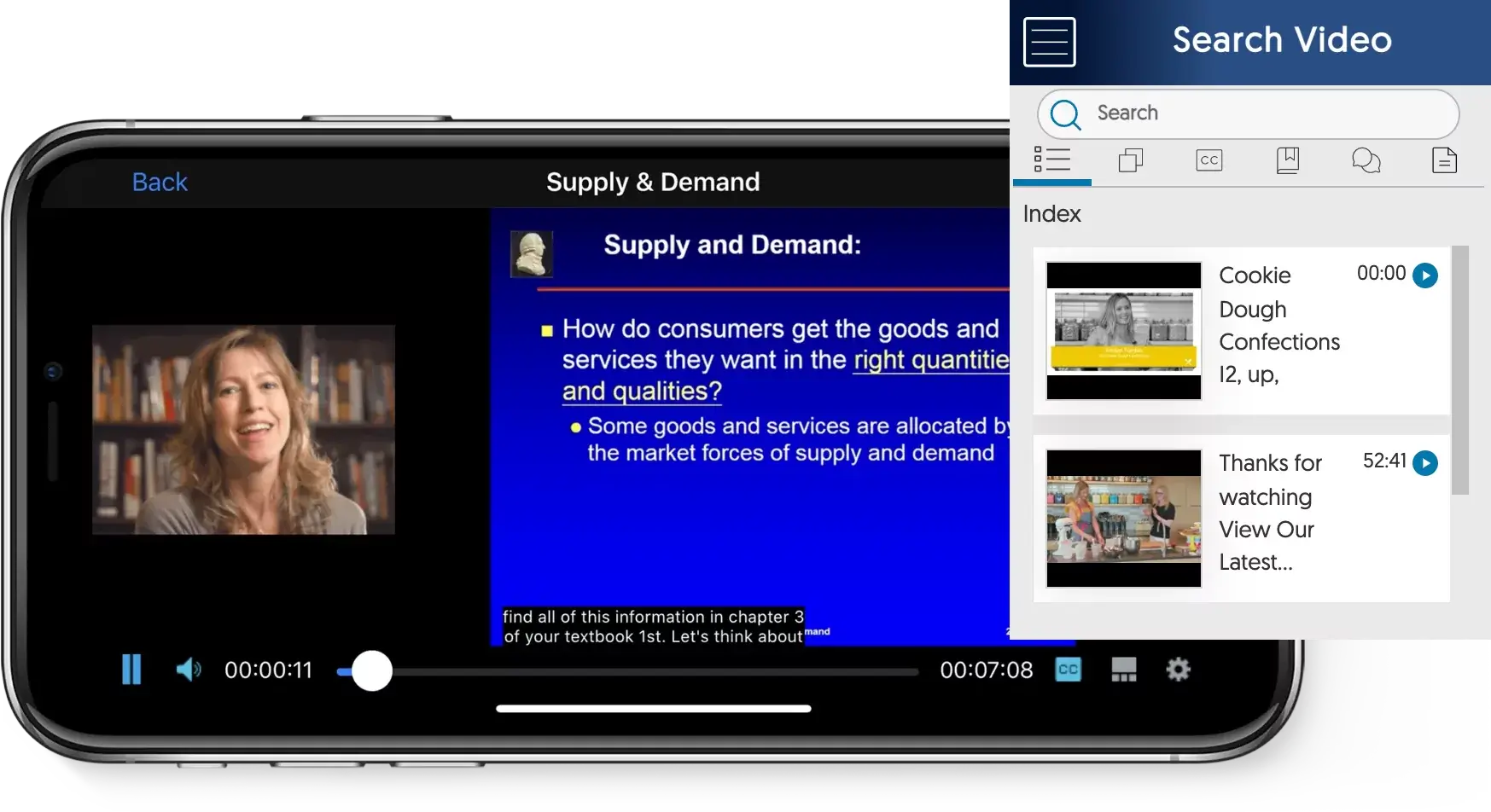
YuJa’s HTML5 Player offers a versatile, customizable experience for users on any device, whether it’s a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, Apple or Android mobile device. The HTML5 Player is available for both single-stream and multi-stream video recordings, and can be branded to match the institution’s colors. Users can easily modify the viewing experience to meet their own needs by resizing windows, expanding or reducing the Sidebar, and toggling thumbnails and captioning on or off.
In addition, the HTML5 video editor is non-destructive, which means you can roll back mistakes. This is a benefit for students in rural areas where the internet connection may cut out, as it prevents loss of content. Below are some of the other widespread benefits of HTML5 for institutions and students:
Benefits for Institutions
While users may see the benefits of HTML5 technology in the user experience, some of the benefits of HTML5 provide institutions with improved functionality and ease-of-use.
- Branding and Customization: HTML5 technology facilitates color customization of the Media Player, including navigation bars, EnterpriseTube, and adding customization by departments to help make the library and video player have the look and feel of your organization.
- Accessibility: HTML5 offers increased accessibility options and 508 compliance, necessary in today’s world.
- Implementation of Mobile Programming: With full playability on a range of devices, HTML5 enables institutions to offer lecture captures and other programming on desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices.
Benefits for Users
HTML5 offers an ideal solution for students to view media on any device with a versatile and functional video experience. Users will see all of the following with HTML5:
- S
 horter Loading Times: HTML5 provides a faster and better viewing experience than other types of video players, with reduced buffering times, even for users on slower internet connections.
horter Loading Times: HTML5 provides a faster and better viewing experience than other types of video players, with reduced buffering times, even for users on slower internet connections. - Enhanced Playability: Since HTML5 technology is browser-based, it works effectively on nearly any system, including Windows, iOS, and Android. Streaming is accessible on both computers and mobile devices.
- Reduced Battery Drain: Playing video in an HTML5 player requires less battery power, whether the user is streaming video on a laptop, tablet, or smartphone.
- Additional Interactivity Options: HTML5 streams provide interactivity through captions, subtitles, thumbnails, and various playback controls that students can adjust based on their preferences.
Bring Lectures to Students On the Go with YuJa’s Mobile Apps
Bringing educational tools to students, where they are and when they have time available provides them with the support they need to succeed in higher education. YuJa offers native mobile apps for both iOS and Android devices, which enable instructors and students alike to create recordings, upload media and download content for offline review.
THE YUJA MOBILE APP EMPOWERS STUDENTS AND INSTRUCTORS
The YuJa app is an ideal addition to the YuJa learning platform. It enables students to access:
- Course lecture captures.
- Uploaded external video content from the Media Channel.
- Social learning features, including real-time discussions.
Additionally, the Video Platform offers a HTML5-based media player designed for optimal device playback. They provide adaptive bitrate streaming, network-sensing technology and interactive capabilities.
Users can simply download the YuJa app from the Apple App Store for iOs or the Google Play store for Android devices and log in using their SSO, either with their established YuJa login or a login provided via email (for institutions that rely on LTI-Integration). This maintains login for a set duration of time, offering students increased ease of access.
YUJA MOBILE APPS PROVIDE REAL-WORLD APPLICATIONS
The YuJa mobile app facilitates learning in a wide variety of situations with exceptional practicality for hands-on training in various fields since the device and lectures can accompany the student wherever they go.
- With the mobile app, a medical student can watch or re-watch a procedure or demonstration from multiple angles. This provides ongoing support for students during training, improving their ability to learn and maximizing the effectiveness of hands-on training.
- During student teaching or teaching practicums, students in the education field can take techniques and lessons from lectures with them to their new classrooms to support their students.
- For engineering and other technical students, integrated presentation media mean that lecture captures can bring diagrams and blueprints home, to the lab, or to the office on a mobile device.
How YuJa’s Enterprise Video Platform Enables Differentiated Instruction
But what does it really mean?
Differentiated instruction, also known as differentiated education, simply means that teachers identify and take into consideration each student’s individual learning style, strengths, needs and interests, and then develops lessons to ensure students have opportunities to learn using their preferred style.
 Well-known educator and speaker Carol Ann Tomlinson is known for her work in differentiated instruction. In her book, “How to Differentiate Instruction in Academically Diverse Classrooms,” Tomlinson explains, “At its most basic level, differentiating instruction means ‘shaking up’ what goes on in the classroom so that students have multiple options for taking in information, making sense of ideas, and expressing what they learn. In other words, a differentiated classroom provides different avenues to acquiring content, to processing or making sense of ideas, and to developing products so that each student can learn effectively.”
Well-known educator and speaker Carol Ann Tomlinson is known for her work in differentiated instruction. In her book, “How to Differentiate Instruction in Academically Diverse Classrooms,” Tomlinson explains, “At its most basic level, differentiating instruction means ‘shaking up’ what goes on in the classroom so that students have multiple options for taking in information, making sense of ideas, and expressing what they learn. In other words, a differentiated classroom provides different avenues to acquiring content, to processing or making sense of ideas, and to developing products so that each student can learn effectively.”
The model has a lot in common with other pedagogical approaches, particularly ones in which teachers vary approaches to teaching the same material that appeals to different students in the same classroom, such as response-to-intervention, data-driven instruction and scaffolding.
YuJa and Differentiated Learning
Using tools like the YuJa Enterprise Video Platform, teachers can provide differentiated learning in a variety of ways, such as:
- Lecture capture, which facilitates classroom flipping and microlessons;
- Social learning, which allows real-time discussion and promoted media engagement; or
- Video conferencing, which offers engaging options for virtual lessons, desktop sharing, collaboration and more.
Quizzes help assess what students understand as they progress, and detailed analytics offer insights into how to tweak instruction based on areas where students are struggling.
YuJa’s Video Platform also makes it easy to incorporate additional learning materials, like online videos, for students requiring additional review or support to gain understanding. Those same tools enable instructors to offer more information to students seeking a deeper understanding of the material.
How YuJa Caters to Various Learning Styles
Students learn differently. While some are auditory learners, others are visual or kinesthetic learners. YuJa’s lecture capture technology meets the needs of each type of learner.
Visual Learning: Visual learners can read the auto-captions on lecture captures. Some visual learners respond best to images, like tables, maps and charts, and others to written words. Word-based learners are called visual-linguistic learners, while those who respond best to images are visual-spatial learners. Since YuJa incorporates all aspects of presentation media, lecture captures include your tables, charts, images and more. In addition, file upload technology makes it easy to provide visual learners with access to PowerPoint presentations and other visual aids.
Auditory Learning: Auditory listeners can listen to lecture captures and re-listen as needed. Since auditory learners learn less effectively from the written word, lecture captures can provide a key tool for these learners. In addition, the YuJa Learning Channel enables you to incorporate other types of video learning for auditory learners.
Kinesthetic Learning: Kinesthetic learners can engage with video quizzes, video creation, and online assignments. In addition, mobile access to YuJa lectures means that kinesthetic learners can take their lectures on the move, walking or even watching a lecture from the gym or wherever they best learn.
YuJa Facilitates Collaboration in the Classroom and Beyond
What is Collaborative Learning?
 According to Cornell University’s Center for Teaching Innovation, collaborative learning is an educational approach that involves students working together in pairs or small groups to solve a problem, complete a task or create a product.
According to Cornell University’s Center for Teaching Innovation, collaborative learning is an educational approach that involves students working together in pairs or small groups to solve a problem, complete a task or create a product.
Benefits include:
- Development of higher-level thinking, oral communication, self-management, and leadership skills.
- Promotion of student-faculty interaction.
- Increase in student retention, self-esteem, and responsibility.
- Exposure to and an increase in understanding of diverse perspectives.
- Preparation for real life social and employment situations.
Collaborative Learning Transfers to the Workplace
The collaborative learning approach carries from the classroom directly into the office, creating individuals capable of working effectively together and solving workplace problems as a team. It encourages cooperation, communication, and makes the best of each person’s strengths.
A LinkedIn Learning study showed that talent developers, executives and people managers all agree that training for soft skills, such as collaboration, communication and leadership are a top priority. Further:
- 68% of employees prefer to learn at work
- 58% prefer to learn at their own pace
- 49% of employees prefer to learn at the point of need
Providing avenues in the workplace to meet these objectives is vital to a successful office environment in which everyone thrives.tudents who graduate prepared to work effectively in a collaborative environment are desirable employees. The communication skills, etiquette and cooperation mastered through collaborative learning will take students from the classroom to the office with grace and ease.
How YuJa’s Suite of Products Integrates into Collaborative Learning
YuJa integrates aspects of collaborative learning into the classroom environment through the Enterprise Video Platform, where each learner has the opportunity to actively participate in the classroom experience.
- Access to file uploads, video chats, and shared files allow students to work in groups, to interact, and to make active progress on course work.
- Real-time whiteboards enable participants to draw and annotate within a live Video Conference session ideal for one-on-one office hours, small group collaborations, and large-scale video conferencing.
- YuJa’s Video Conferencing Platform for the classroom enables multimedia collaboration with no application downloads or installs.
YuJa makes it easy to allow students to collaborate and solve problems. For students in brick-and-mortar classrooms or in a virtual environment, the social learning environment improves access to and opportunities for collaboration, thereby creating richer, more flexible and streamlined learning.
The Value of a Cloud-Hosted Video Platform
Cloud Hosting vs On-Prem Hosting
 Cloud hosting involves using a network of connected remote and/or virtual devices, which makes the technology scalable, reliable and on-demand. Because information is spread across data centers, if a hosting site goes offline, others compensate to keep your system up and running smoothly. No two organizations’ needs are the same and cloud hosted services can be tailored in an unlimited way, with flexibility in areas like architecture, space and security. The servers are owned and managed by a vendor.
Cloud hosting involves using a network of connected remote and/or virtual devices, which makes the technology scalable, reliable and on-demand. Because information is spread across data centers, if a hosting site goes offline, others compensate to keep your system up and running smoothly. No two organizations’ needs are the same and cloud hosted services can be tailored in an unlimited way, with flexibility in areas like architecture, space and security. The servers are owned and managed by a vendor.
The alternative to cloud hosting is on-premise, or “self-hosted” solutions. This option uses local resources to run software on computers physically located on-premise of the organization. The organization must have a space for the servers, known as a data center, or use a virtual private server or virtual dedicated service to locate on premise software, but hosting is still provided by the organization’s own hardware.
Cloud Hosting is a Value Driven Solution
Cloud hosting has become increasingly popular for a number of reasons, including speed of innovation, operating cost and security.
“Cloud hosting removes barriers to entry for businesses and organizations, which no longer have to find and train their own team to support their infrastructure,” said Nathan Arora, Chief Business Officer at YuJa, Inc. “It’s a smart, cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.”
Speed of innovation: Cloud solutions allow for rapid innovation with fewer risks of disruption. Members of your organization can focus on innovating rather than reacting to daily minutia of technical issues that arise when self-hosting. You can scale up or down on demand, test ideas quickly and keep moving toward your organization’s next great idea.
Internal operating cost: Using the cloud shifts what is normally a capital expenditure to an operating expenditure, lowering the initial costs, as well as ongoing IT management and support costs. On-prem hosting requires a trained team, whereas with cloud solutions, everything is handled through the vendor.
Level of data security and privacy: Cloud platform solutions like the YuJa Cloud ensure data security and privacy, which includes having third-party audits to ensure the highest level of security.
The YuJa Video Cloud
Designed by engineers, scientists and PhDs with a track-record of deploying large-scale distributed systems, each tool within our Enterprise Video Platform leverages the YuJa Cloud to deliver a high-impact user experience. The YuJa Cloud is the backbone of our entire video-powered platform, including lecture capture, media management, live streaming, video conferencing, social learning and mobile video tools.
IntelliVid Research Discusses Future of Video in Higher Education With YuJa
Steve Vonder Haar, a Senior Analyst with IntelliVid Research, recently interviewed YuJa Co-Founder and Chief Business Officer, Nathan Arora, on the evolving role of video in education, how the market has changed since the pandemic, and the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education technology tools.
YuJa is a great example. It started with a purpose-built Video Platform for teaching and learning, and for delivering educational content at scale. Since then, several products have been added to the suite of tools, including those that focus on delivering accessible content, managing data and storage, test proctoring, and audience engagement.
While the company continues to serve the higher education market, the focus has been on deepening its impact. Rather than expanding horizontally, YuJa “serves a single audience with a number of different products that serve them more effectively, all within the same realm,” Arora said.
“The pandemic accelerated a need to become more digital not just in teaching and learning, but in all interactions.”
The pandemic led to a big increase in utilization of video in higher education, as institutions worldwide were forced to get on board. After nearly 100 percent utilization, usage has gone down, but not to pre-pandemic levels. The pandemic accelerated a need to become more digital not just in teaching and learning, but in all interactions.
“That means our products become much more pervasive, but it also means there’s a need to do things better and more cost effectively. So if you’re going to manage larger volumes of content, you’re going to make content a central part of the strategy, you have to make that more accessible,” Arora said. In addition, everyone should benefit from media, and with a centralized, enterprise-deep strategy, they can.
Vonder Haar also asked how AI would impact the development of video related applications and how it has impacted YuJa’s roadmap and go-to-market strategy. AI is already being used in technologies like automatic transcriptions and captioning, and to extract valuable insights. In higher education, though, Arora said institutions tend to take a more measured approach to implementing new technologies.
Fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement is essential to keep pace with evolving technologies and pedagogical trends. In the future, Arora said he sees AI being used in other meaningful ways that keep the academic rigor of the institution, but noted it will be institution-led.
Using Video Outside of the Classroom to Engage and Support Potential Students
Reaching Potential Students
Video offers an ideal way to reach out to potential students. Unlike text and photos, video offers an immersive experience where potential students can see your campus and the surrounding community.
Instructors and staff can introduce themselves, and the traditional campus tour can go online for students and their families who may not be able to visit in person, including those internationally.
Consider integrating video content that shows:
- Campus facilities: What do the dorms look like? How big are the classrooms and classes? How active is the student center? Videos of your campus can help answer these questions for potential students.
- Faculty and programs: For many students, and particularly graduate students, access to skilled researchers and academic faculty is a deciding factor in school choice. Choose faculty to introduce different schools, departments, courses, and who they can expect to learn from if they attend your institution.
- The campus community: Show potential students their future classmates. Get video of fun events like the annual water balloon fight, or a charity fundraiser to share with potential students.
Attracting International Students
”Creating rich video content of your campus, community and the surrounding town can give international students an orientation of the area long before their flights touch down.”
At many colleges and universities, international students make up a significant percentage of the student body. For an international student, there may not be an opportunity to visit the campus. Creating rich video content of your campus, community and the surrounding town can give international students an orientation of the area long before their flights touch down.
To appeal to potential international students, share more than just information about your campus and community.
- Interview current international students, and consider offering some interviews (or captions) in the native language.
- Show meetings of international student groups, clubs and activities.
- Include tours of graduate student housing, including off-campus housing if you’re able.
- Share success stories of current students or alumni, highlighting impactful community initiatives, and showcasing campus events and activities contribute to a vibrant and engaging culture.
- Use testimonials and behind-the-scenes glimpses to help ignite curiosity and drive students to take the next step.
- Consider hosting a Q&A session for prospective students.
Creating an Alternative to the Campus Visit

While many students will make a campus visit, either before accepting their admission or the summer before they attend, this isn’t an option for all families. A well-rounded video library can provide students with access to much of the information available during a campus visit.
- Use lecture capture technology to capture classes and workshops offered during campus visits.
- Record a campus tour. Take the time to explore, just like a potential student might.
- Get as many people as you can, instructors and students, on camera to help highlight the campus and its community.
- Create video tutorials for the first day on campus, from moving in to picking up a parking pass and student ID. That way, all students can quickly find how to do these tasks whether they were able to attend orientation or not.
Interactive video experiences can help educational institutions build trust and credibility while compelling potential students to consider the institution as a valuable partner in their educational journey. Using video for non-instructional purposes presents an opportunity for colleges and universities to attract and support students at all stages of their educational journey.
The Role of Live Streaming in Higher Education
In terms of education, though, live streaming is still a fairly new endeavor. Live streaming refers to streaming media in real time. Before the mid-2010s, institutions typically didn’t offer live streaming because often, students didn’t have the internet bandwidth required to support it. “Advances in features like adaptive bitrate streaming, which provides the ability to record while simultaneously streaming for later viewing, have allowed colleges and universities to expand live streaming programs to the benefit of students,” said Nannette Don, Director of Sales. Now, even if students can’t stream a lecture at all, they still have the option to securely download and review the lesson. There are a number of other benefits to live streaming in higher education:
“Prior to the 21st century, if a learner couldn’t make it to the physical building for their education, they simply missed out. But the evolution of the internet and technology, hardware — and later software — have modernized video in education, making education more flexible and accessible.”
Live Streaming Removes Barriers
Colleges, universities and other enterprises have been able to implement live streaming as one of a variety of tools to aid students in their education. Higher education institutions can reach more students than ever before, which is an advantage both to students and the institutions. Students who have full time jobs, family obligations, health issues or a myriad of other barriers to education can now live stream their instruction with only access to a stable internet connection.
Live Streaming Builds Trust
When a classroom lecture is streamed live, students have the advantage of observing things they might not be able to pick up in other forms of communication like email or a phone call. By reading facial expressions and mannerisms, students can better understand tone and infer meaning through what is said and demonstrated live.
Live Streaming Creates Connections
Students in online classes can sometimes have feelings of disengagement or apathy. By offering ways to engage with one another and the professor, students can create meaningful connections just like if they were in a traditional classroom setting. Teachers can offer real time question and answer sessions, office hours and more through various software applications. “YuJa supports multi-source live streaming, which includes casting to multiple sources from a number of angles, truly giving students the feeling that they’re in that classroom or space,” Don highlighted, adding that students can be as interactive as they want during the discussions.
How Are Colleges and Universities Using Live Streaming?
As you can imagine, the possibilities with live streaming educational content are endless. With creativity and a willingness to learn and participate, higher education institutions are finding unique, innovative ways to implement live streaming.

Nevada State College is a prime example of a school using live streaming to make a difference in the lives of students and their families. Nevada State College places a special emphasis on the advancement of a diverse and under-served student population. Because of its diverse immigrant population, the college was host to a naturalization ceremony for new citizens of the United States. And because many had relatives in other countries, the college live streamed the momentous event, allowing families to celebrate with their loved ones.
Indiana State University is another institution that has taken a progressive approach to non-traditional methods of learning using technology like live streaming to further every student’s education, whether it occurs on campus or via online courses and programs. The university has a number of students who earn their degree without ever stepping foot on campus. For nursing students, that means completing their practicums virtually. Students can record and securely send their recording to their instructor for evaluation.


The student counselors at Texas Wesleyan University’s Community Counseling Center, along with faculty and staff, have continued to train the next generation of counselors by providing virtual services for more than 320 clients.
The role of live streaming in education has quickly evolved from a “nice to have” to a must have, particularly during the current pandemic. Whether it’s a sporting event, fitness class, concert, commencement or a traditional classroom lesson, live streaming enhances the experience for students who can’t be present in person or who want to view the event later.
Be unstoppable in your quest to educate students. With a drive to better serve learners, combined with YuJa’s video enterprise platform, anything is possible.
The Legacy of Judy Heumann, “The Mother of Disability Rights”
As a child in 1949 living in Brooklyn, New York, Heumann contracted polio and began using a wheelchair for mobility. At the age of five, she was deemed a “fire hazard,” and denied entry to school, according to her website. As a child, her mother advocated for her and she was eventually allowed into school. Though this was among the first discriminatory acts against her, it was not the last.
“Some people say that what I did changed the world, but really, I simply refused to accept what I was told about who I could be. And I was willing to make a fuss about it.”
“It was still a radical claim that disabled people didn’t see themselves, or their conditions, as something to be pitied. Or that they insisted what most held them back wasn’t their health condition but society’s exclusion — maybe attitudes that they were less capable to do a job, go to college or find romance; or a physical barrier, like a sidewalk without a curb cut,” said NPR’s Joseph Shapiro in an article about Heumann.
Shapiro shared that he wrote an article about disability rights in 1987 in which Heumann said “Disability only becomes a tragedy when society fails to provide the things we need to lead our lives — job opportunities or barrier-free buildings, for example,” she said. “It is not a tragedy to me that I’m living in a wheelchair.” The article was not published because the idea she relayed seemed so “unexpected and strange.”
Starting a Revolution
In 1970, after Heumann passed her oral and written teaching exams, but she ultimately failed the medical exam where she was again deemed a “fire hazard.” This time, examiners said she would not be able to evacuate children or herself during an emergency. Heumann sued the board of education to allow her to become a teacher. The New York Times headline read “Woman in Wheel Chair Sues to Become Teacher” and the article noted she would be the city’s first teacher in a wheelchair. Her lawyers said the case was the first such civil rights suit ever filed in a federal court.
She was instrumental in the development and passage of Section 504, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Rehabilitation Act, and the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which “have been advancing the inclusion of disabled people in the US and around the world and fighting to end discrimination against all those with disabilities.”
“Section 504 became a model for the ADA, which would extend the principles of non-discrimination to all public accommodations, employment, transportation, communications and access to state and local government programs,” NPR said. That means if you’ve ever used an elevator in a subway station or busy public area, if you used the curb cuts to more easily get on a sidewalk, or if you’ve used the accessible restrooms in a public space, you’ve benefited from the ADA. Closed captions, transcripts, and website accessibility, are all other examples of services for disabled people that benefit everyone.
When Richard Nixon vetoed the 1972 Rehabilitation act, Heumann helped lead a protest that shut down traffic in Manhattan. She also launched a 26-day sit-in at a federal building in San Francisco to get Section 504 of the revived Rehabilitation Act enforced. “(The sit-in) has often been described as the longest nonviolent occupation of a federal building in American history,” The New York Times reported.
More Advocacy Efforts
Heumann never stopped at securing rights for herself, but continued her work for others. Heumann co-founded the World Institute on Disability (WID), which was among the first global disability rights organizations led by people with disabilities. The institute is “dedicated to designing, building, and supporting whole community solutions by removing barriers to include people with disabilities.”
Heumann served the Clinton Administration as the Assistant Secretary for the Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services in the Department of Education from 1993 to 2001. From 2002 to 2006, she was the World Bank’s first Adviser on Disability and Development.
She was appointed by President Barack Obama as the first Special Advisor for International Disability Rights in the U.S. Department of State, a position she held from 2010-2017. She also was the Director for the Department on Disability Services and responsible for the Developmental Disability Administration and the Rehabilitation Services Administration.
The American Civil Liberties Union said she traveled to countries on every continent to help change the way people perceive those with disabilities and to help remove barriers they face in their everyday lives. Between 2000 and 2015, 181 countries passed disability civil rights modeled after the ADA, according to NPR.
Documentary and Book Release
Just before the pandemic, Heumann was featured in a documentary released at the 2020 Sundance film festival. “Crip Camp: A Disability Revolution,” was about Heumann and others who attended a summer camp (Camp Janed) for children with disabilities in the Catskills. Heumann later was a counselor at the camp. Camp Janed became “the beginnings of a revolution.”
“What I want is for the book and the film — and other books and films — to allow people to recognize the real absence of representation of disability in media, broadly speaking”
Heumann also has a memoir, “Being Heumann: An Unrepentant Memoir of a Disability Rights Activist.” Heumann told The Cut, “What I want is for the book and the film — and other books and films — to allow people to recognize the real absence of representation of disability in media, broadly speaking. Black disabled people, Latino disabled people, Asian disabled people, indigenous disabled people, disabled people with visible and invisible disabilities — they’re pretty absent. And yet, in the United States, it’s more than 20 percent of our population. Disability is something that all families experience, temporarily or permanently.”
“Some people say that what I did changed the world,” she wrote, “But really, I simply refused to accept what I was told about who I could be. And I was willing to make a fuss about it.”
Learn more about Judy Heumann on her website.
Photos courtesy of Judithheumann.com
Find the Right Fit: Lecture Capture vs. Video Podcasting
To get the most out of your video solution, it is important to choose the right recording tools for the right environment and to ensure everything works together seamlessly to create consistency, to allow for ease in training, and to increase adoption throughout your institution.
Lecture Capture is an Ideal Classroom Solution
 Lecture capture, or the recording and archiving of audio and video components of a lecture, is ideal in the classroom, whether you opt for a traditional or flipped classroom structure. The YuJa hardware appliance integrates into all classroom multimedia equipment, streaming your lecture directly to the cloud, while software capture provides organizations with the ability to record anywhere and capture multiple inputs. With automated scheduling, you can capture lectures without any additional work.
Lecture capture, or the recording and archiving of audio and video components of a lecture, is ideal in the classroom, whether you opt for a traditional or flipped classroom structure. The YuJa hardware appliance integrates into all classroom multimedia equipment, streaming your lecture directly to the cloud, while software capture provides organizations with the ability to record anywhere and capture multiple inputs. With automated scheduling, you can capture lectures without any additional work.
Lecture capture offers the following advantages:
- If you’re recording lectures in a brick-and-mortar classroom, you’re likely to find lecture capture the most practical choice, as you’ll typically be working from a podium in the classroom.
- If you opt for software-based lecture capture, you will need to initiate the software; however, it will work on any device. Record with a camera or document camera, or record your smart board or external web camera, or any combination of devices.
- Lecture capture integrates into other classroom multimedia resources, including the SmartBoard.
- Your students can easily replay, pause and rewind lecture captures for future use.
Additionally, the Software Capture and Browser Capture tools used for lecture capture can be used to create podcasts.
Video Podcasting is Another Powerful Tool to Support Learning
“Podcast” refers to any software and hardware combination that allows automatic downloading of audio files for listening at a user’s convenience.
Video podcasting is ideal for review videos or enrichment materials to supplement work in the classroom; however, it can also be an ideal way to engage with students online, especially in remote learning environments.
Use cases and advantages include:
- Video podcasting using your own webcam and microphone is an ideal way to offer information to your students.
- The videos stream into the cloud and are stored as part of your learning channel.
- You can integrate files and materials you’re using directly into your video podcast, or even use an interactive sketchpad to illustrate lessons. This makes video podcasting a practical supplement to classroom learning or an ideal way to present short, manageable lessons for online-only students.